
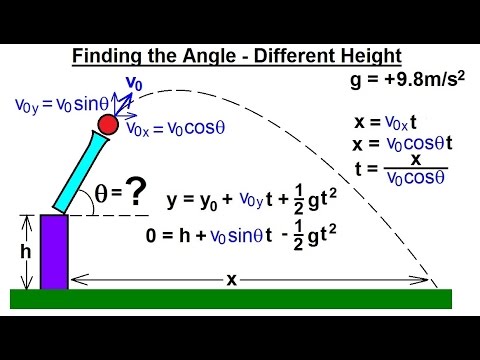
We will analyze the motion of the projectile using the kinematic equations, separated into x- and y-components. Projectile motion only occurs when there is one force applied at the beginning on the trajectory, after which the only interference is from gravity. the projectile is moving forward in the x-direction with constant velocity while it is accelerated downward due to gravity. The path that the object follows is called its trajectory.

To solve projectile motion problems, we analyze the motion of the projectile in the horizontal and vertical directions using the one-dimensional kinematic equations for x and y. Motion in any given direction is independent of motion in a perpendicular direction. Projectile motion is a form of motion where an object moves in a bilaterally symmetrical, parabolic path. Projectile motion is the motion of an object subject only to the acceleration of gravity, where the acceleration is constant, as near the surface of Earth.(ii) Moves under the influence of gravity.\)(t) can be written as a vector sum of the one-dimensional velocities v x(t), v y(t), v z(t) along the x, y, and z directions.
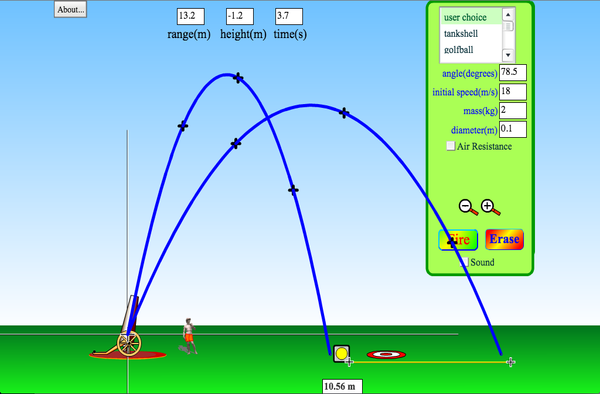
(b) the horizontal distance traveled by the ball. Projectile motion is one type of 2-D motion under constant acceleration. (a) the total time the ball is in the air. List equations of motion to see which ones to use. (i) Follows a parabolic path (trajectory). Problem (1): A person kicks a ball with an initial velocity of 15 m/s at an angle of 37 above the horizontal (neglecting the air resistance). Projectile motion is completely described by these equations for the velocity and position com- ponents. Overview of projectile motion:Īny motion having the following conditions is called a projectile motion.
#2d projectile motion equations free
On the Earth’s surface, the constant acceleration a is equal to g 9.8 m/s 2, and an object undergoing projectile motion is in free fall with this as the only. Using the kinematic equations below, one can predict the distance to where the projectile will land based upon the initial speed, total time, and angle of. There is also a pdf for worksheets with answers. Projectile motion is how physicists describe two-dimensional motion where the only acceleration the object in question experiences is the constant downward acceleration due to gravity. Every single question is designed to be a complete guide on this topic without referring to your textbook. The most complete guide on solving projectile motion problems for high school and college students. Projectile Motion Practice Problems for AP Physics


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
